Introduction
Apache Tomcat is an application server that can be used to serve Java
applications to web users. It is an open implementation of the Java
Servlet and JavaServer Pages specs that were developed by Sun
Microsystems.
If you develop Java applications, Tomcat is a quick and easy way to
serve them in a full server environment specifically designed for that
purpose.
In this guide, we will install Tomcat and do some basic configuration
on a Debian 7 VPS. To complete this tutorial, you will have to have a
normal user with sudo privileges. Follow this guide to learn
how to create users on a Debian system.
Install Apache Tomcat
In this guide, we will install Tomcat version 8 and its associated
packages. Luckily, these are included in the default Debian
repositories.
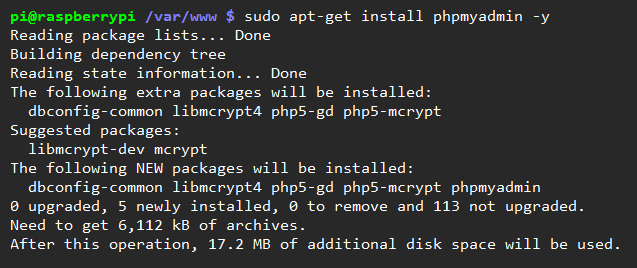
To get the basic package, we can update our package source list and then install the main package:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install tomcat8
This is all we need to do to get to the default Tomcat page. Our
installation is not complete yet, but you can take a look at the default
Tomcat page by going to your IP address or domain followed by
:8080 in your web browser:
your_domain_or_ip:8080
In order to take advantage of more of Tomcat's features, we will install some additional Tomcat packages.
These will allow us to use a web interface to control Tomcat. It
will install some documentation and examples that we can also access
through the web interface as well.
sudo apt-get install tomcat8-admin tomcat8-examples tomcat8-docs
The Tomcat documentation also suggests that you install Apache Ant,
which is a build tool for Java applications, and a version control
system of some sort. We will choose git:
sudo apt-get install ant git
These will help you build your Java applications and keep the code organized.
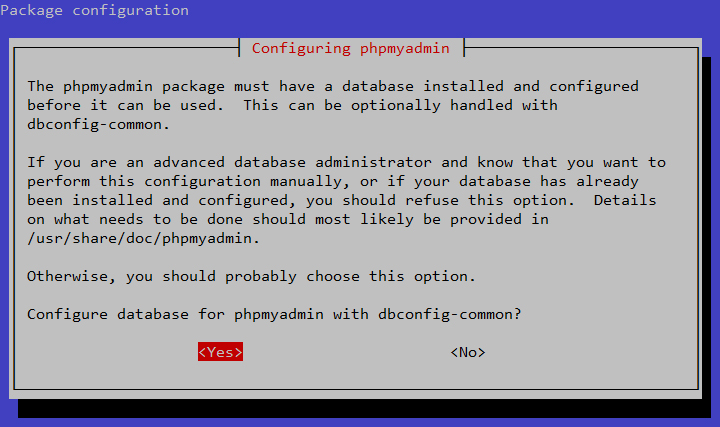
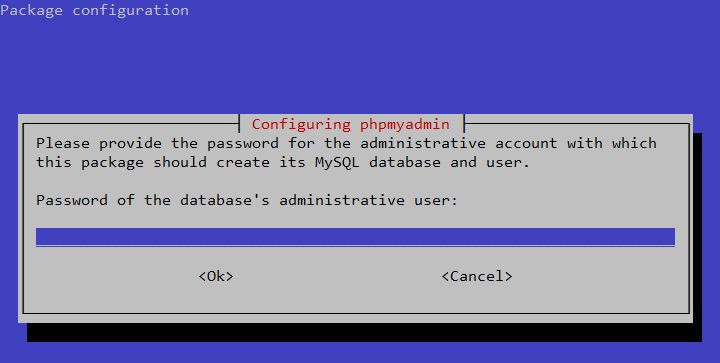
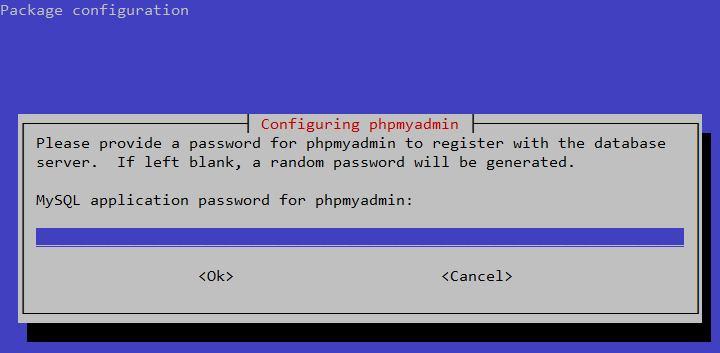
Before we can begin using some of the features we installed, we need
to configure our server with a user and password. Tomcat does not do
this by default for security reasons.
The configuration is very simple. We need to edit a file called
tomcat-users.xml. Open it with an editor like this:
sudo nano /etc/tomcat8/tomcat-users.xml
Inside, you will find a heavily commented user configuration file. In fact, the only portions of the file that are
not comments are:
<tomcat-users>
</tomcat-users>
As you might expect, we need to define a user between these two
lines. We will give this user access to the web interfaces. We can
define a user like this:
<tomcat-users>
<user username="admin" password="password" roles="manager-gui,admin-gui"/>
</tomcat-users>
Choose whatever username and password you would like. This will
provide you with login credentials that allow you to access the
management panels.
Save and close the file when you are finished.
We should restart Tomcat in order to implement our changes:
sudo service tomcat8 restart
We should stop Tomcat to implement our changes:
sudo service tomcat8 stop
Test the Web Interface
Once you have installed Tomcat and configured the user login, you can
access the main page by going to your server IP address or domain name
followed by
:8080 like this:
your_domain_or_ip:8080
You will see the same default Tomcat page that you saw earlier (if you checked):